Diabetes Mellitus Management Goals: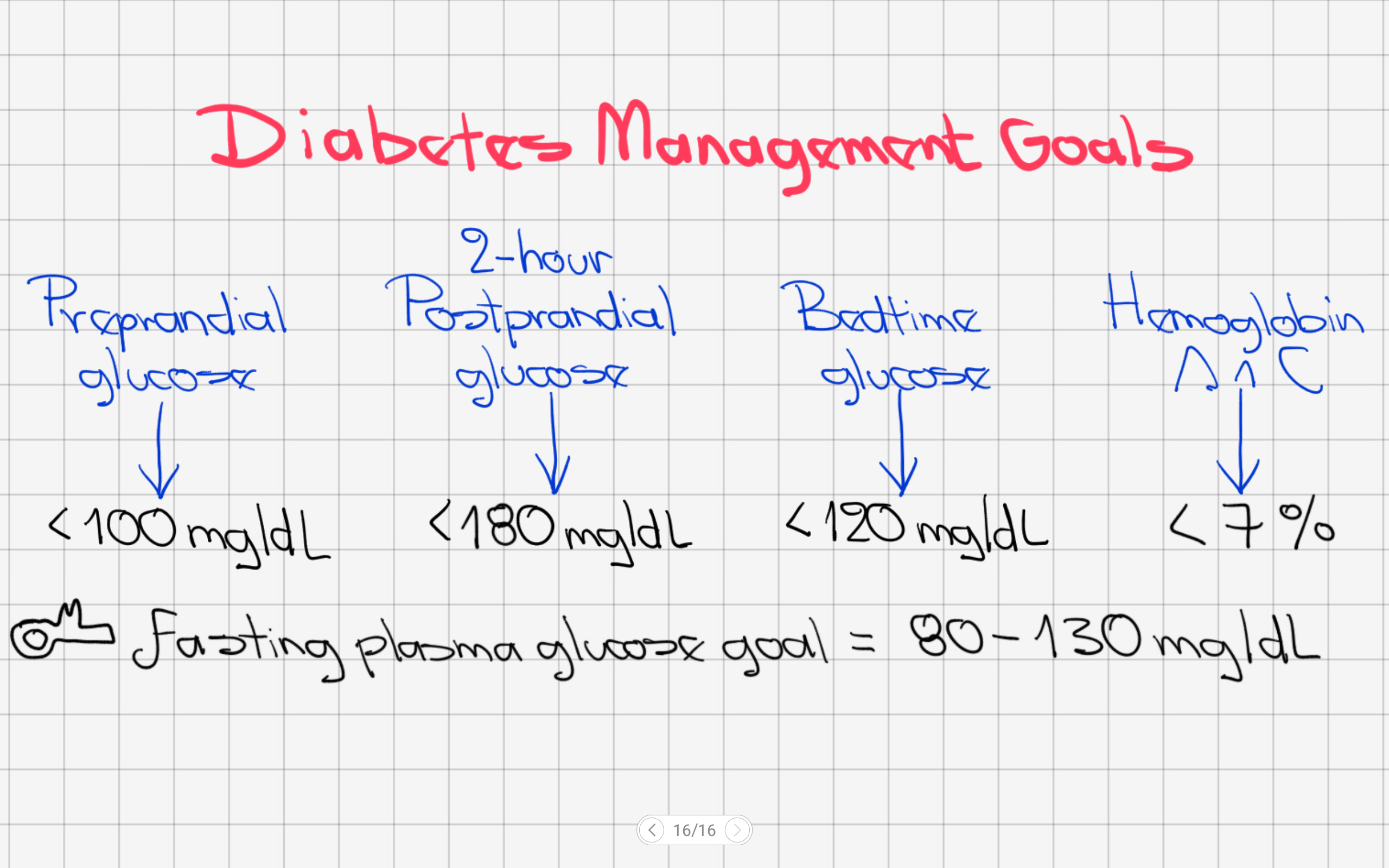
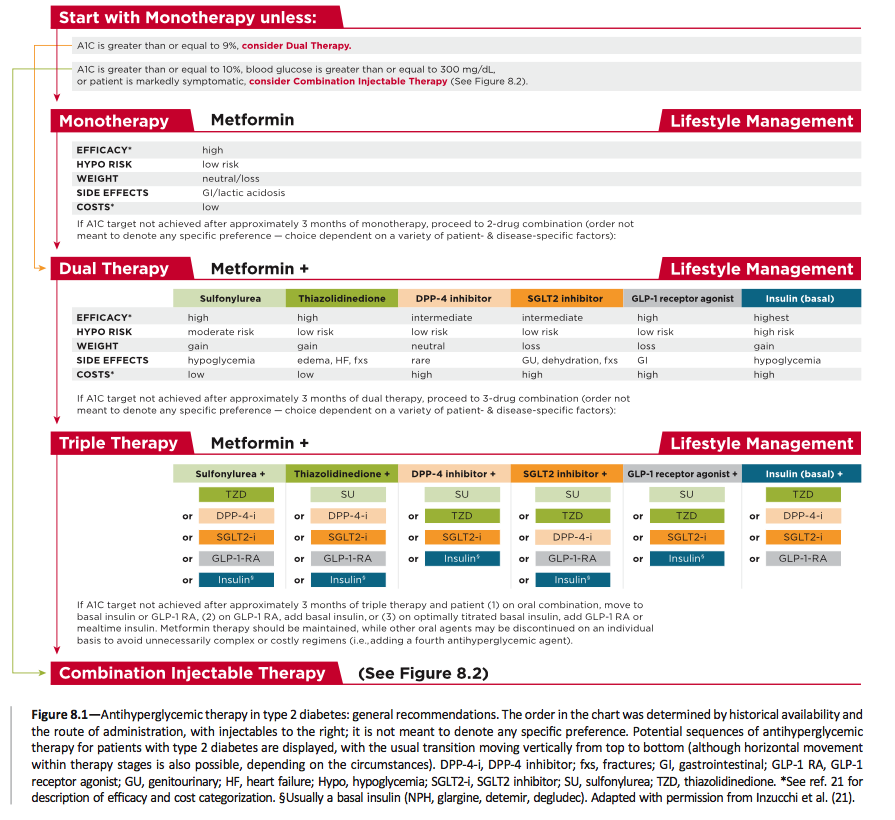
Pharmacologic Therapy in Diabetes Mellitus type 2 recommendations:
- Metformin is the first-line treatment unless contraindicated, it should be started at the time of diagnosis always. The three major contraindications for Metformin use are:
- Impaired renal function: Abnormal creatinine absolute values or creatinine clearance, eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m².
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) requiring pharmacologic therapy.
- Advanced age (>80 years old).
- The HbA1C levels help in deciding which pharmacologic treatment we can start:
- A1C < 9 but > 7 (diabetic range): Start lifestyle modifications + Metformin monotherapy.
- A1C ≥ 9 but <10: Dual therapy.
- A1C ≥ 10: Combination injected therapy.
American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes – 2017, anti-hyperglycemic therapy recommendations:
Non-insulin therapy: Expected A1C level decrease (from major to minor):
- Metformin: 1.5
- Thiazolidinediones (TZD’s): 0.5 – 1.5
- Glinides: 0.5 – 1.5
- Sulfonylureas (SU): 1.2
- DPP-4 inhibitors: 1
- GLP-1 agonists: 1
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: 0.8
- Bromocriptine: 0.7
- Bile acid sequestrants (BAS): 0.5
Anti diabetic therapy: Hypoglycemia risk by medication (from highest to lowest):
- Insulin: (Highest).
- Sulfonylureas (Moderate).
- Thiazolidinediones (Low).
- GLP-1 agonists (Low).
- SGLT-2 inhibitors (Low).
- DPP-4 inhibitors (Low).
- All the rest: (Low risk).
Latest posts by Juan Chango Azanza (see all)
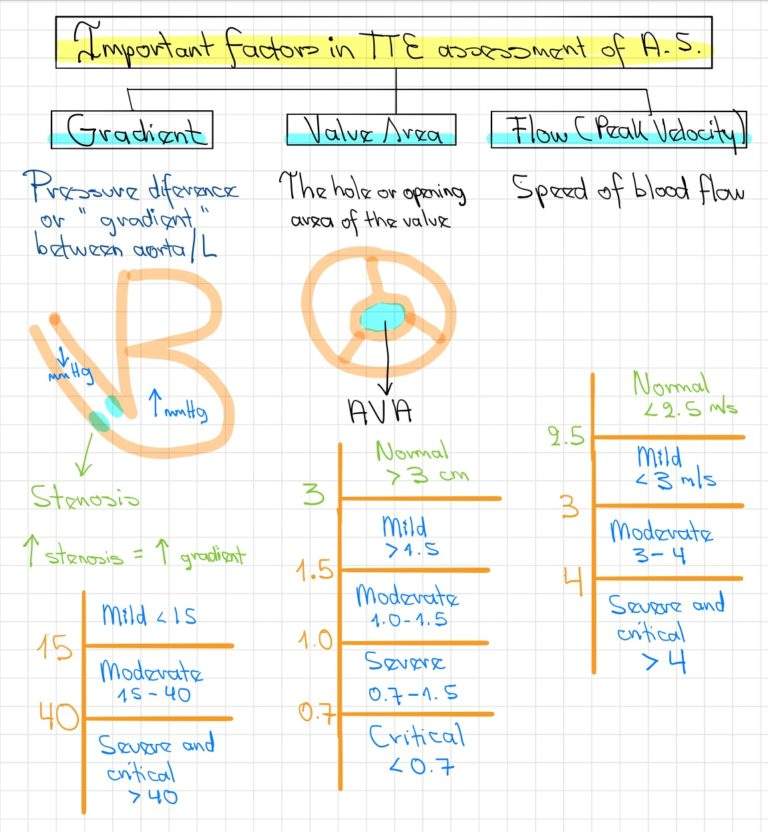
- Aortic Stenosis Severity Classification - 09/22/2020
- Carboplatin (Paraplatin) - 04/07/2019
- How to test for Vitamin D deficiency? - 09/29/2018