These are the blue sheet, physical exam, diagnostic studies and differential diagnosis needed for a hearing loss case in the USMLE Step 2 CS exam:
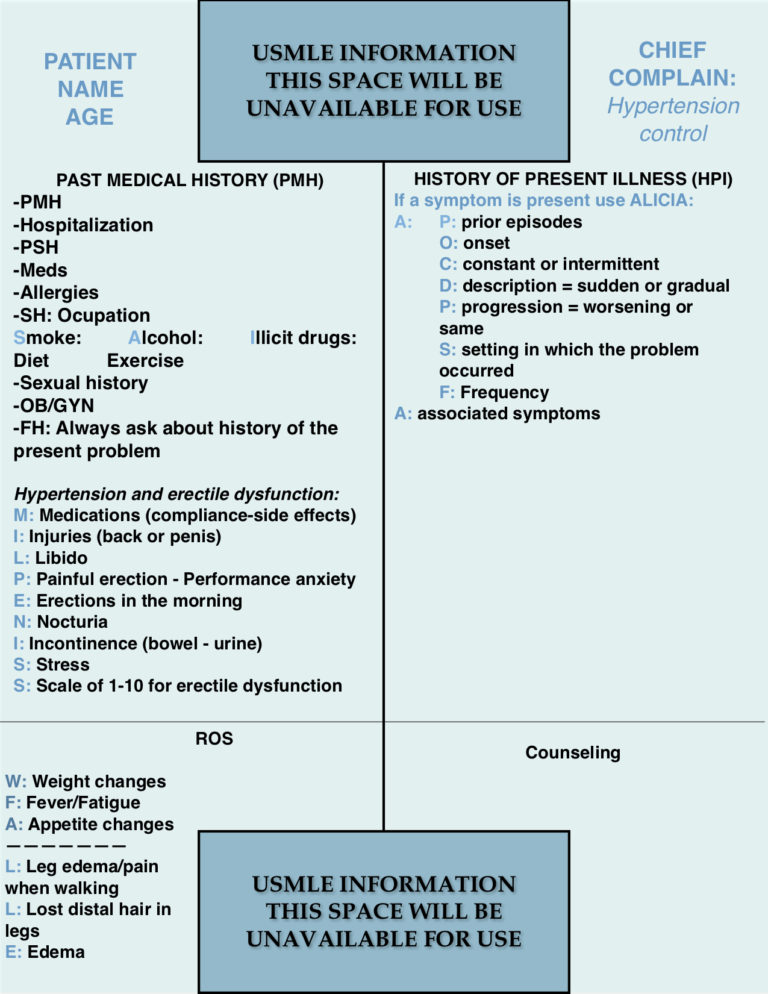
BLUE SHEET HEARING LOSS:

HEARING LOSS MNEMONIC:
“NOISE HITS THE (DA = DD) eaRS”
N: Noise exposure present or past.
O: Objects inserted into the ear recently.
I: Infections recently, mostly upper respiratory infections.
S: Sound type (high, low-pitched sounds).
E: Ear pain or secretions recently, history of chronic ear infections.
H: Headaches.
I: Imbalance.
T: Trauma/Treatment tried for the hearing loss: hearing aids, cleaning of the ears.
S: Source of sound recognition.
D: Distortion of sounds/Voice distortion when listening to people or TV.
D: Dizziness.
R: Ringing in the ears.
S: Spinning (vertigo).
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
1. HEENT:
- EOM look for nystagmus.
- Ear: Inspection, palpation.
- Weber and Rinne test.
2. Lungs:
- Auscultation
3. Heart:
- Auscultation
4. Neurologic:
- Cranial nerves, CN VIII by talking from behind is very important.
- Motor: Strength.
- Sensory.
- DTR’s.
- Cerebellar: Heel to shin and finger to nose tests.
POSSIBLE DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES:
- CBC.
- ESR.
- VDRL, RPR.
- Audiometry.
- Tympanography.
- CT of the head.
- Brainstem auditory evoked potentials.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
Differentiate conductive and sensorineural hearing loss:
CONDUCTIVE HEARING LOSS:
- Impacted cerumen.
- Otitis media.
- Tympanic membrane perforation.
- Otosclerosis.
- Foreign body insertion.
- Cholesteatoma.
- Tympanosclerosis.
SENSORINEURAL HEARING LOSS
- Presbycusis.
- Cochlear nerve damage.
- Ototoxicity (mostly drugs: aminoglycosides, diuretics).
- Meniere’s disease.
- Acoustic neuroma.
- Diabetes.
I hope this information was helpful for you, please leave your comments below and I will try answering as soon as possible. Start practicing early the mnemonics for easier memorization. Good luck with your studies.
- Aortic Stenosis Severity Classification - 09/22/2020
- Carboplatin (Paraplatin) - 04/07/2019
- How to test for Vitamin D deficiency? - 09/29/2018